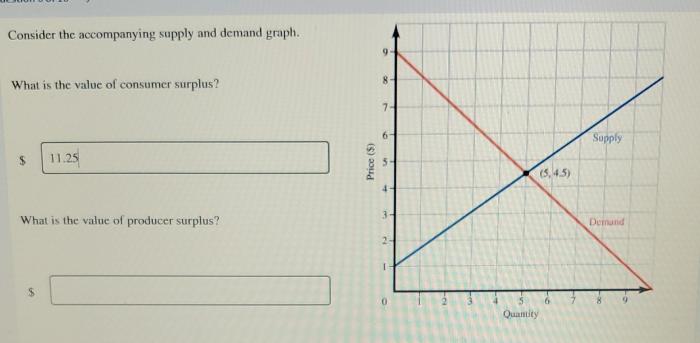
Economic growth can be pictured in the accompanying diagram by, a multifaceted phenomenon that has captivated the minds of economists and policymakers for centuries. It encompasses a wide range of factors, indicators, and implications that shape the economic landscape of nations.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of economic growth, exploring its key drivers, measurement techniques, and the complex relationship it shares with sustainability, inequality, innovation, globalization, and technology.
Economic Growth and its Factors
Economic growth refers to the sustained increase in the productive capacity of an economy over time, resulting in a higher level of goods and services produced. Key factors that contribute to economic growth include:
- Capital accumulation: Investment in physical capital (machinery, infrastructure) and human capital (education, skills)
- Technological progress: Innovation and technological advancements that increase productivity
- Labor force growth: Increase in the number of workers and their productivity
- Natural resources: Availability and efficient use of natural resources such as minerals, energy, and land
Examples of countries that have experienced significant economic growth include China, India, and South Korea.
Economic Growth Indicators
Economic growth is measured using various indicators, including:
- Gross domestic product (GDP): Total value of goods and services produced in an economy within a given period
- Gross national product (GNP): Total value of goods and services produced by residents of a country, regardless of where they are produced
- Gross domestic income (GDI): Total income earned by residents of a country, regardless of where it is produced
- Per capita income: GDP or GNP divided by the population of a country
| Indicator | Calculation | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| GDP | Sum of all final goods and services produced in an economy | Measures overall economic activity and growth |
| GNP | GDP + Net income earned abroad | Measures the income earned by a country’s residents |
| GDI | GDP + Net income earned abroad + Depreciation | Measures the total income available to a country’s residents |
| Per capita income | GDP/GNP/GDI per person | Measures the average standard of living in a country |
Economic Growth and Sustainability
Economic growth and environmental sustainability are often seen as competing goals. However, it is possible to balance both by:
- Promoting renewable energy and reducing carbon emissions
- Adopting sustainable agricultural practices
- Investing in green infrastructure and technologies
Examples of countries that have successfully balanced economic growth with sustainability include Denmark, Costa Rica, and Sweden.
Economic Growth and Inequality
Economic growth can lead to income inequality, as the benefits of growth are often not evenly distributed. Causes of income inequality include:
- Differences in education and skills
- Discrimination in the labor market
- Concentration of wealth in the hands of a few individuals
Strategies to mitigate income inequality while promoting economic growth include:
- Investing in education and skills training
- Enacting policies that promote equal opportunities
- Implementing progressive taxation systems
FAQs: Economic Growth Can Be Pictured In The Accompanying Diagram By
What are the key factors that contribute to economic growth?
Key factors include capital accumulation, technological advancements, labor force growth, and human capital development.
How is economic growth measured?
Common indicators include Gross Domestic Product (GDP), GDP per capita, and economic growth rate.
What is the relationship between economic growth and sustainability?
Economic growth can strain natural resources and contribute to environmental degradation, highlighting the need for sustainable practices.