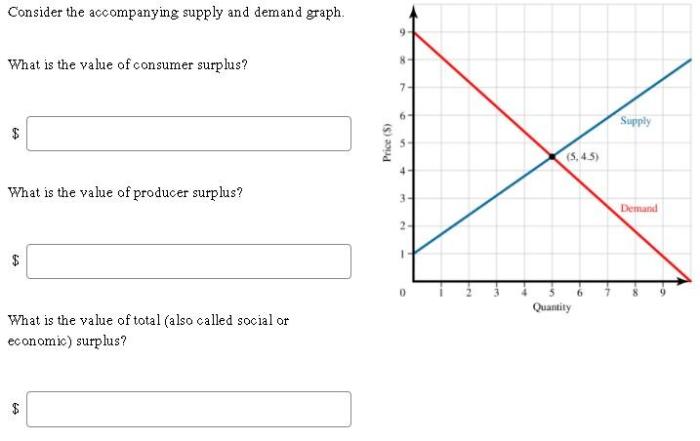
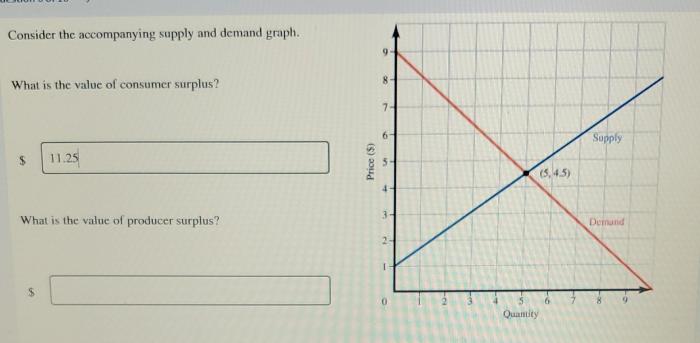
Consider the accompanying supply and demand graph. – Consider the accompanying supply and demand graph, a graphical representation of the interplay between supply and demand forces in a market. This graph serves as a valuable tool for understanding market dynamics, predicting price and quantity outcomes, and evaluating the impact of external factors.
The supply and demand graph provides a snapshot of the relationship between the quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply and the quantity that consumers are willing and able to demand at various prices.
Supply and Demand Graph Analysis
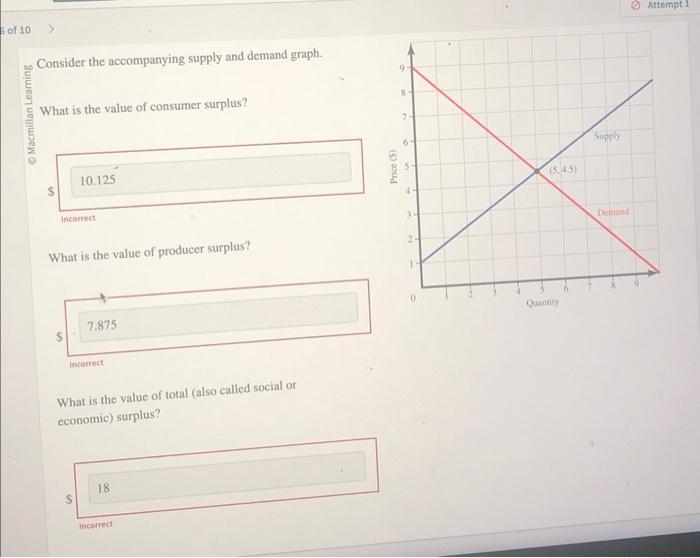
The accompanying supply and demand graph depicts the relationship between the quantity of a good or service supplied by producers and the quantity demanded by consumers at different prices. The equilibrium point represents the intersection of the supply and demand curves, indicating the price and quantity at which the market is in balance.
Factors Shifting Supply and Demand Curves
- Changes in production costs, technology, or government policies can shift the supply curve.
- Changes in consumer preferences, income, or expectations can shift the demand curve.
Impact of Market Changes
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
Changes in supply or demand will affect the equilibrium price and quantity. An increase in supply, for example, will lead to a lower equilibrium price and higher equilibrium quantity.
Elasticity
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of supply or demand to price changes. Elastic markets are highly responsive, leading to significant changes in quantity supplied or demanded with small price changes.
Real-World Examples
- Increased demand for smartphones has shifted the demand curve to the right, leading to higher prices and increased production.
- Technological advancements have shifted the supply curve for solar panels to the right, resulting in lower prices and increased adoption.
Market Interventions
Government Interventions
Governments can intervene in markets to influence supply and demand through measures such as:
- Price ceilings: Maximum prices set by the government to protect consumers.
- Price floors: Minimum prices set by the government to support producers.
- Subsidies: Government payments to producers or consumers to encourage production or consumption.
Consequences of Interventions, Consider the accompanying supply and demand graph.
- Price ceilings can lead to shortages and black markets.
- Price floors can lead to surpluses and reduced efficiency.
- Subsidies can distort market prices and create dependency.
Market Failures
Causes and Consequences
Market failures occur when the market fails to achieve an efficient outcome. Causes include:
- Externalities: Costs or benefits that are not reflected in market prices.
- Public goods: Goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, leading to underprovision.
- Monopoly power: When a single producer has significant control over the market, leading to higher prices and reduced output.
Consequences include:
- Inefficient allocation of resources.
- Reduced consumer welfare.
- Environmental degradation.
Role of Government
Governments can intervene to address market failures through:
- Regulations: Laws and policies to correct externalities or prevent monopolies.
- Provision of public goods: Governments can provide goods and services that the private sector cannot or will not.
- Antitrust laws: Laws to prevent or break up monopolies and promote competition.
Questions Often Asked: Consider The Accompanying Supply And Demand Graph.
What is the equilibrium point on a supply and demand graph?
The equilibrium point is the point where the supply curve and demand curve intersect. It represents the price and quantity at which the market is in balance, with no excess supply or demand.
How can changes in supply or demand affect the equilibrium price and quantity?
An increase in supply will shift the supply curve to the right, leading to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity. Conversely, a decrease in supply will shift the supply curve to the left, resulting in a higher equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium quantity.
Similarly, an increase in demand will shift the demand curve to the right, leading to a higher equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity. A decrease in demand will shift the demand curve to the left, resulting in a lower equilibrium price and a lower equilibrium quantity.
What is elasticity, and how does it impact market outcomes?
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied or demanded to changes in price. A highly elastic supply or demand curve indicates that a small change in price will lead to a large change in quantity. Conversely, a highly inelastic supply or demand curve indicates that a small change in price will lead to a small change in quantity.