The root in the term prolactinoma means – The term “prolactinoma” holds a rich etymological history, with its root “prolact” offering a glimpse into the intricate functions of the human body. This exploration delves into the origin and meaning of “prolact,” examining its connection to the hormone prolactin and the implications for understanding the pathophysiology of prolactinomas.
Prolactin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, particularly lactation and reproduction. The root “prolact” stems from the Latin words “pro” (meaning “for”) and “lac” (meaning “milk”), reflecting its primary function in stimulating milk production in lactating women.
Etymology of the Term “Prolactinoma”
The term “prolactinoma” originates from two Greek roots: “prolactin” and “-oma.” “Prolactin” refers to the hormone prolactin, while “-oma” signifies a tumor or neoplasm.
The root “prolactin” is derived from “pro,” meaning “for,” and “lactin,” which pertains to milk production. This reflects the primary role of prolactin hormone in stimulating milk production in lactating women.
Role of Prolactin in the Body: The Root In The Term Prolactinoma Means
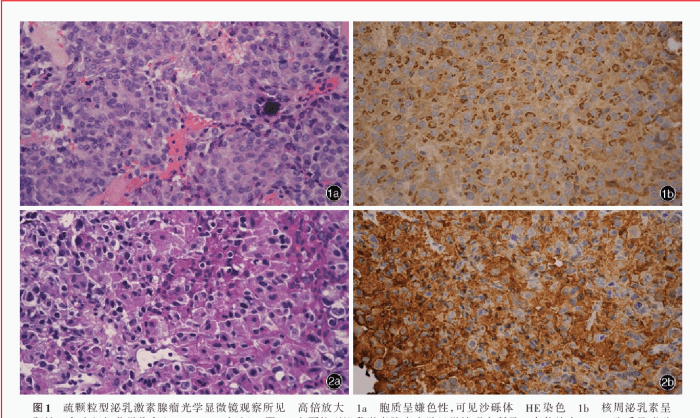
Prolactin is a hormone primarily responsible for regulating milk production in women after childbirth. It also plays a role in other physiological processes, including:
- Lactation
- Immune function
- Stress response
- Metabolism
Prolactin exerts its effects by binding to receptors on target organs and tissues, such as the mammary glands and immune cells.
Pathophysiology of Prolactinoma
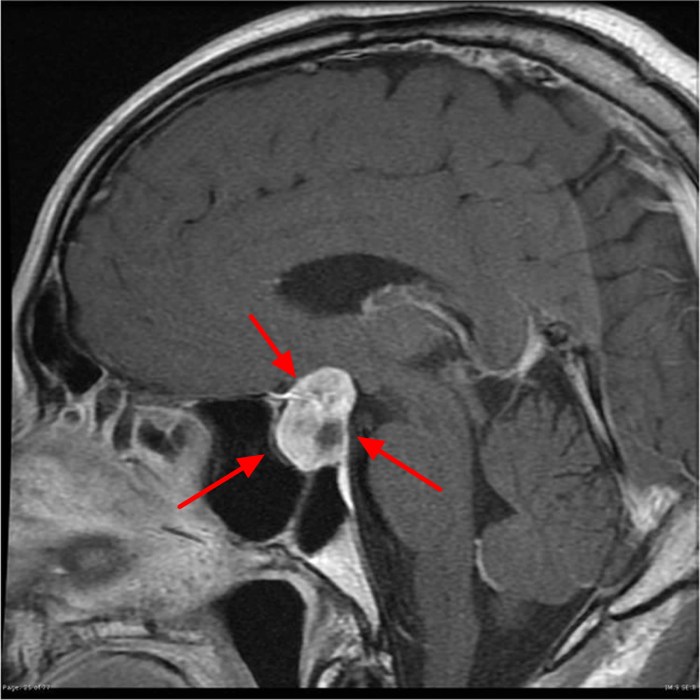
A prolactinoma is a benign tumor that develops in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. It is characterized by excessive production of prolactin hormone.
Prolactinomas can cause hormonal imbalances, leading to clinical manifestations such as:
- Amenorrhea (loss of menstrual periods) in women
- Galactorrhea (milk production in non-lactating women)
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction in men
Clinical Presentation of Prolactinoma
The clinical presentation of prolactinoma varies depending on the size and location of the tumor. Common symptoms include:
Hormonal Effects, The root in the term prolactinoma means
- Amenorrhea
- Galactorrhea
- Infertility
- Erectile dysfunction
Non-Hormonal Effects
- Headaches
- Vision problems
- Fatigue
- Nausea
Diagnosis and Management of Prolactinoma
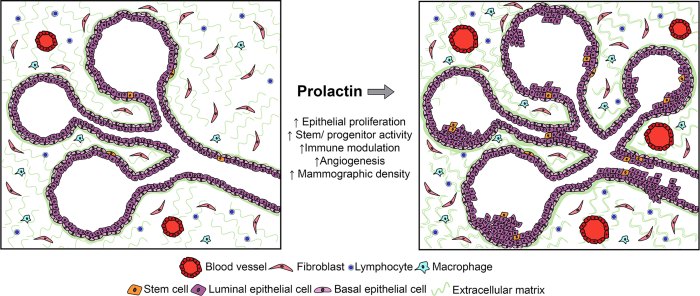
The diagnosis of prolactinoma is typically made based on:
- Medical history and physical examination
- Blood tests to measure prolactin levels
- Imaging techniques, such as MRI scans, to visualize the pituitary gland
Treatment options for prolactinoma include:
- Medication to lower prolactin levels
- Surgery to remove the tumor
- Radiation therapy to shrink the tumor
Prognosis and Follow-Up of Prolactinoma
The prognosis of prolactinoma patients is generally good. With appropriate treatment, most patients can achieve remission of symptoms and restore hormonal balance.
Regular follow-up care is essential to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and manage any potential complications, such as recurrence of the tumor or long-term effects of prolactin excess.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of the root “prolact” in the term “prolactinoma”?
The root “prolact” signifies the connection to prolactin, a hormone primarily involved in milk production. In the context of prolactinomas, it highlights the hormonal imbalances caused by the tumor’s overproduction of prolactin.
How does the root “prolact” relate to the function of prolactin hormone?
The root “prolact” directly translates to “for milk,” reflecting the hormone’s primary role in stimulating lactation. It underscores the close association between prolactin and its physiological functions.
What are the implications of understanding the etymology of “prolactinoma”?
Grasping the etymological roots of “prolactinoma” enhances our comprehension of the tumor’s pathophysiology. It provides a deeper understanding of the hormonal imbalances and clinical manifestations associated with prolactinomas.